If you’re considering a residential or commercial solar installation, understanding the typical size of solar panels is an important first step. The length and width of solar panels can vary widely, and size determines the number of panels that can fit on a roof and the system’s overall energy output.
At Solar Insure, choosing the right solar panel is critical in your journey toward clean and sustainable energy. To help you make the best decision for your energy needs, we’ve analyzed data from 100 solar panels featured on our AVL (Approved Vendor List).
Our AVL represents a select group of manufacturers and panel models thoroughly vetted for quality, reliability, and performance by our strict underwriting guidelines.
While various factors influence solar panel dimensions, our analysis gives you a helpful overview of typical sizes. It helps you understand how the length, width, and depth ranges relate to wattage, efficiency, and installation considerations.
With this analysis, we hope to empower consumers and businesses with the information they need to choose the best option for their solar needs.
Key Takeaways
- Most solar panels fall within a length range of 67.8 to 93.9 inches and a width range of 39 to 51.3 inches. Lower wattage panels tend to be on the smaller end of these ranges, while higher wattage panels tend to be larger.
- Solar panel thickness is relatively consistent, ranging from 1.18 inches to 1.57 inches. The most common depth is 1.38 inches.
- Panel dimensions are influenced by wattage, cell technology, and panel design, which means sizes will always vary, even between panels with similar wattage or efficiency ratings.
- Understanding typical solar panel dimensions can help you plan your solar installation. Knowing the general size range of panels can help homeowners or installers assess roof space requirements and make smart panel selections.
Solar Panels: Dimensions, Efficiency, & Load
| Model | Efficiency (%) | Power (W) | Length (in) | Width (in) | Debth (in) | Weight (lbs) | Load Rating (Pa) | Bifacial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aptos DNA-108-BF10 | 20.74 | 400-410 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 48.5 | 5400 | Yes |
| Aptos DNA-108-MF10 | 20.47 | 390-400 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 48.5 | 5400 | No |
| Aptos DNA-120-BF10 | 20.55 | 440-450 | 74.9 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 50 | 5400 | Yes |
| Aptos DNA-120-MF10 | 20.62 | 430-440 | 74.9 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 52.9 | 5400 | No |
| Aptos DNA-120-MF26-370W | 20.66 | 370-370 | 69.1 | 40.9 | 1.4 | 46.3 | 5400 | No |
| Aptos DNA-144-BF10-550W-DG | 21.29 | 550-550 | 89.6 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 71.2 | 5400 | Yes |
| Aptos DNA-144-BF26 | 20.65 | 440-450 | 82.5 | 40.7 | 1.4 | 53.1 | 6200 | Yes |
| Aptos DNA-144-MF26-440W | 20.21 | 440-440 | 82.5 | 40.9 | 1.4 | 55.3 | 5400 | No |
| Canadian Solar CS1U | 20.4 | 400-420 | 81.8 | 39.1 | 1.4 | 51.6 | 2400 | No |
| Canadian Solar CS1Y | 20.1 | 390-405 | 79.6 | 39.2 | 1.4 | 49.8 | 2400 | No |
| Canadian Solar CS3N | 20.8 | 380-425 | 76.4 | 41.3 | 1.4 | 49.6 | 2400 | No |
| Canadian Solar CS3U | 20.2 | 380-400 | 78.7 | 39.1 | 1.4 | 49.6 | 3600 | No |
| Canadian Solar CS3W | 20.8 | 435-460 | 83 | 41.3 | 1.6 | 54.9 | 3600 | No |
| Canadian Solar CS6.1-54THM | 23 | 445-470 | 70.9 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 50.7 | 6000 | No |
| Canadian Solar CS6R | 20.7 | 380-405 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 49.4 | 5000 | No |
| Elin Energy ELNSM54M-HC | 21.25 | 405-415 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 47.4 | 5400 | Yes |
| Elin Energy ELNSM54M-HC US MIN | 21.25 | 405-415 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 47.4 | 5400 | Yes |
| JA Solar JAM54S31 MR | 20.7 | 380-405 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 47.4 | 5400 | No |
| JA Solar JAM72S01 PR | 20.1 | 370-390 | 77.2 | 39 | 1.6 | 49.6 | 3600 | No |
| JA Solar JAM72S09 PR | 19.8 | 375-395 | 78.3 | 39.6 | 1.6 | 49.8 | 5400 | No |
| JA Solar JAM72S10 MR | 20.4 | 390-410 | 79.3 | 39.2 | 1.6 | 45.6 | 5400 | No |
| Jinko 54HL4-B | 21.51 | 400-420 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 48.5 | 2400 | No |
| Jinko 6RL3-B | 20.96 | 380-400 | 73 | 40.5 | 1.4 | 47.2 | 2400 | No |
| Jinko 72L-V | 19.92 | 375-395 | 77.9 | 39.4 | 1.6 | 49.6 | 5400 | No |
| Jinko HBL-V | 19.88 | 380-400 | 79.1 | 39.4 | 1.6 | 49.6 | 2400 | No |
| Jinko HL-4-B | 22.27 | 425-445 | 69.4 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 48.5 | 4000 | No |
| Longi LR4-72HBD | 20.9 | 425-455 | 82.4 | 40.9 | 1.4 | 60.6 | 5400 | No |
| Longi LR4-72HBH | 21.4 | 445-465 | 82.4 | 40.9 | 1.4 | 53.6 | 5400 | No |
| Longi LR5-54HABB | 21.3 | 390-415 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 49.6 | 5400 | No |
| Longi LR5-54HPB | 21.5 | 400-420 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 45.9 | 5400 | No |
| Longi LR6-72HBD | 19.1 | 360-385 | 79.5 | 39.2 | 1.2 | 58 | 5400 | Yes |
| Longi LR6-72HPH | 19.3 | 365-385 | 78.9 | 39.2 | 1.4 | 50.7 | 5400 | No |
| Longi LR6-72PH | 19.6 | 360-380 | 77 | 39 | 1.6 | 49.6 | 5400 | No |
| Maxeon SPR-MAX3 | 22.2 | 410-420 | 71.3 | 41.2 | 1.6 | 46.7 | 2400 | No |
| Maxeon SPR-MAX6 | 23 | 420-445 | 73.7 | 40.6 | 1.6 | 48.1 | 3600 | No |
| Meyers Burger Black | 21.5 | 375-395 | 69.6 | 41 | 1.4 | 43.4 | 5400 | No |
| Meyers Burger White | 21.7 | 380-400 | 69.6 | 41 | 1.4 | 43.4 | 4000 | No |
| Mission Solar HT0B | 21 | 400-410 | 67.8 | 44.7 | 1.4 | 41.9 | 5400 | No |
| Mission Solar SX5R | 19.3 | 375-385 | 75.1 | 41.1 | 1.6 | 48.5 | 5400 | No |
| Mission Solar SX6Z | 19.1 | 410-420 | 82.1 | 41.5 | 1.6 | 51.6 | 5400 | No |
| Mission Solar SX9R | 19.9 | 390-400 | 75.1 | 41.5 | 1.6 | 48.5 | 5400 | No |
| Mission Solar SX9Z | 19.6 | 420-430 | 82.1 | 41.5 | 1.6 | 51.6 | 5400 | No |
| Panasonic EVERVOLT H Series 400W | 21.6 | 400-400 | 71.7 | 40 | 1.2 | 45.2 | 5400 | No |
| Panasonic EVERVOLT H Series 410W | 22.2 | 410-410 | 71.7 | 40 | 1.2 | 45.2 | 5400 | No |
| Panasonic EVERVOLT HK2 Black 420W | 21.7 | 420-420 | 71.7 | 40 | 1.2 | 45.2 | 5400 | No |
| Panasonic EVERVOLT HK2 Black 430W | 22.2 | 430-430 | 71.7 | 40 | 1.2 | 45.2 | 5400 | No |
| Panasonic EVERVOLT PK Black 360W | 19.7 | 360-360 | 69.5 | 41.3 | 1.4 | 46.3 | 5400 | No |
| Panasonic EVERVOLT PK Black 370W | 20.3 | 370-370 | 69.5 | 41.3 | 1.4 | 46.3 | 5400 | No |
| Panasonic EVPV HK | 22.2 | 400-410 | 71.7 | 40 | 1.2 | 45.2 | 7000 | No |
| Qcells .PEAK DUO BLK ML-G1 | 20.6 | 385-405 | 74 | 41.1 | 1.3 | 48.5 | 4000 | No |
| Qcells .PEAK DUO BLK ML-G9 | 20.3 | 365-385 | 72.4 | 40.6 | 1.3 | 43 | 4000 | No |
| Qcells EAK DUO BLK ML-G10+ | 21 | 385-415 | 74 | 41.1 | 1.3 | 48.5 | 4000 | No |
| Qcells Q.P EAK DUO L-G8.3/BG | 19.6 | 405-420 | 81.9 | 40.6 | 1.4 | 62.8 | 3000 | Yes |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO L-G5.2 | 19.9 | 380-400 | 79.3 | 39.4 | 1.4 | 51.8 | 2400 | No |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO L-G5.3 | 20.1 | 380-405 | 79.3 | 39.4 | 1.4 | 50.7 | 2400 | No |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO L-G6 | 20.5 | 405-425 | 81.9 | 40.6 | 1.4 | 54 | 5400 | No |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO L-G6.2 | 19.8 | 405-425 | 81.9 | 40.6 | 1.4 | 55.1 | 2400 | No |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO L-G7.2 | 20.1 | 385-405 | 79.3 | 39.4 | 1.4 | 51.8 | 2400 | No |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO L-G7.3 | 20.1 | 285-405 | 79.3 | 39.4 | 1.4 | 50.7 | 2400 | No |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO L-G8.2 | 20.1 | 415-430 | 81.9 | 40.6 | 1.4 | 55.1 | 2400 | No |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO ML-G10.a | 20.9 | 385-410 | 74 | 41.1 | 1.3 | 48.5 | 4000 | No |
| Qcells Q.PEAK DUO ML-G10+ | 21.1 | 395-415 | 74 | 41.1 | 1.3 | 48.5 | 4000 | No |
| Qcells Q.TRON BLK M-G2+ | 22 | 405-430 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 46.7 | 3600 | No |
| REC Solar AA 72 | 21.3 | 420-450 | 81.2 | 40.4 | 1.2 | 52 | 2400 | No |
| REC Solar AA Pure | 21.9 | 385-405 | 71.7 | 40 | 1.2 | 45 | 7000 | No |
| REC Solar AA Pure 2 | 22.2 | 400-430 | 73.4 | 40.9 | 1.2 | 47.6 | 7000 | No |
| REC Solar AA Pure R | 22.3 | 400-430 | 68.1 | 44 | 1.2 | 47.4 | 7000 | Yes |
| REC Solar AA Pure-RX | 22.6 | 450-470 | 68 | 46.1 | 1.2 | 51.6 | 7000 | Yes |
| REC Solar NP3 Black | 20.3 | 390-400 | 74.8 | 40.9 | 1.2 | 47 | 7000 | No |
| REC Solar TP2SM 72 | 20 | 370-400 | 78.9 | 39.4 | 1.2 | 48.5 | 3600 | No |
| SEG Solar 450-BMA-BG | 20.7 | 435-450 | 82.4 | 40.9 | 1.2 | 61.7 | 5400 | Yes |
| SEG Solar BMD-HV | 21.51 | 405-420 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 47.4 | 5400 | No |
| SEG Solar BTD-BG | 22.02 | 415-430 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 52.9 | 5400 | No |
| Silfab BG | 21.4 | 410-410 | 73.4 | 40.5 | 1.4 | 45.9 | 5400 | No |
| Silfab BK | 21.4 | 370-380 | 70.7 | 39 | 1.5 | 41.9 | 2400 | No |
| Silfab HC+ | 20.7 | 400-410 | 75.4 | 40.8 | 1.4 | 47 | 5400 | No |
| Silfab NT | 19.2 | 380-380 | 78.4 | 39.1 | 1.5 | 47.4 | 2400 | No |
| Silfab QD | 22.1 | 420-430 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 46.3 | 5400 | No |
| Silfab QD-DCA | 22.1 | 420-430 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 46.3 | 5400 | No |
| Trina Solar DE09C.07 | 21.1 | 380-405 | 69.1 | 43.1 | 1.2 | 46.3 | 6000 | Yes |
| Trina Solar DE14A(II) | 19.3 | 340-375 | 77.2 | 39.1 | 1.6 | 57.3 | 2400 | No |
| Trina Solar DE14H.08(II) | 19.9 | 345-395 | 78.7 | 39.1 | 1.6 | 50.7 | 2400 | No |
| Trina Solar DE15H(II) | 19.7 | 385-400 | 79.7 | 39.5 | 1.4 | 50.3 | 2400 | No |
| Trina Solar DE15M(II) | 20.7 | 390-415 | 79.3 | 39.2 | 1.4 | 48.5 | 2400 | No |
| Trina Solar NE09RC.05 | 21.5 | 400-430 | 69.4 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 47 | 6000 | Yes |
| Trina Solar NEG9.28 | 21.9 | 400-425 | 69.7 | 43.1 | 1.2 | 47.4 | 6000 | No |
| VSUN Solar 108BMH | 20.75 | 390-405 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 48.1 | 2400 | Yes |
| VSUN Solar 108BMH-BB | 22.02 | 415-430 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 47.2 | 5400 | Yes |
| VSUN Solar 144BMH | 20.37 | 435-450 | 83 | 41.3 | 1.4 | 53.8 | 5400 | Yes |
| Waaree Bi-55-550 Dual Glass | 21.17 | 550-550 | 89.4 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 71.7 | 5400 | Yes |
| Waaree WSMDiB-405 All Black | 20.28 | 405-405 | 69.5 | 41.3 | 1.4 | 48.5 | 5400 | No |
| Waaree WSMT-580 TOPCon N-Type | 21.17 | 580-580 | 89.7 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 70.5 | 5400 | Yes |
| Waaree WSMT-700 N-Type TOPCon | 22.5 | 680-715 | 93.9 | 51.3 | 1.4 | 77.2 | 5400 | No |
| Seraphim N-TOPCon SRP-440-BTD-BG | 22.53 | 440-440 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 40.8 | 5400 | Yes |
| Seraphim N-TOPCon SRP-630-BTZ-BG | 22.5 | 630-630 | 93.9 | 51.3 | 1.4 | 77.2 | 5400 | Yes |
| Seraphim S4 SRP-555-BMA-HV | 21.48 | 555-555 | 89.7 | 44.6 | 1.4 | 63.1 | 5400 | No |
| Seraphim S4 SRP-405-BMD-HV | 20.94 | 405-405 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 47.4 | 5400 | No |
| Seraphim S4 SRP-400-BMD-HV | 20.48 | 400-400 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 47.4 | 5400 | No |
| Solar4America S4A410-108MH10 | 21 | 410 | 67.8 | 44.6 | 1.2 | 46.3 | 5400 | No |
| Solar4America S4A405-72MH5 | 20.91 | 405 | 78 | 39.4 | 1.6 | 48.5 | 5400 | No |
Typical Solar Panel Dimensions: Exploring Length, Width, and Depth
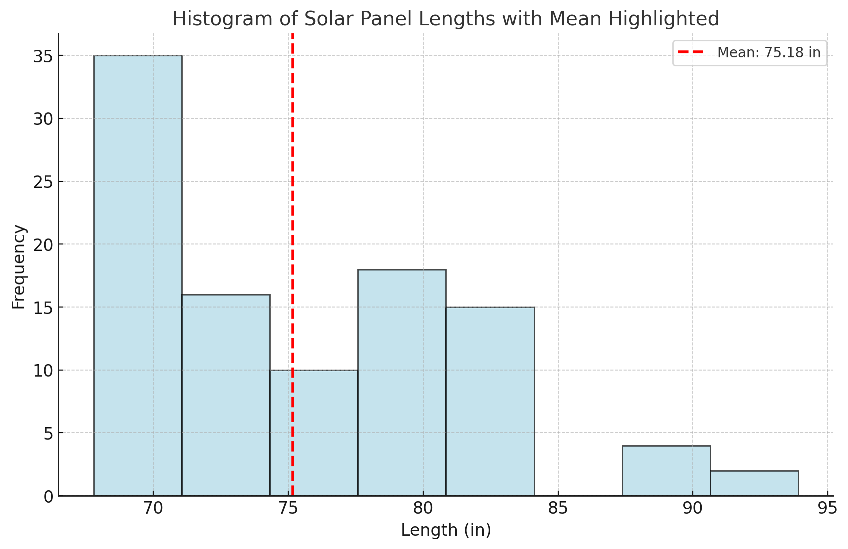
We’ve reviewed solar panel dimensions from various manufacturers. By analyzing the collected data, we can identify the typical ranges for length, width, and depth:
Length:
- The data indicates a broad range of lengths, typically between 67.8 inches and 93.9 inches.
- Panels with lengths around 67.8 to 70.9 inches are more common for lower wattage models.
- As wattage increases, the lengths tend to extend, with panels in the 78.7 to 82.7-inch range becoming more prevalent.
- Some high wattage panels, particularly those exceeding 600W, can reach lengths of 93.9 inches.
Width:
- Solar panel width generally varies between 39.0 inches and 51.3 inches.
- A common width range of 39.1 to 41.5 inches encompasses many models across different wattages.
- Wider panels, such as those exceeding 44.5 inches, are often associated with higher wattage models.
Depth (or Thickness):
- Solar panel depth, or thickness, is relatively consistent, generally ranging from 1.18 to 1.57 inches. Panels with a 1.38-inch (35 mm) depth are quite common.
- Some models, especially those designed for greater durability or specific applications, might have a slightly greater depth of 1.57 inches.
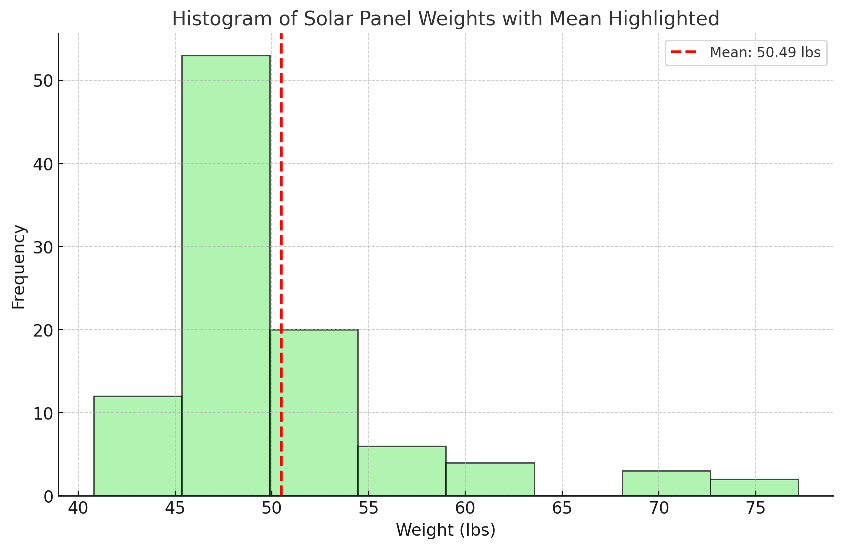
Typical Weight Range for Solar Panels
We also have weight information for various solar panels. The “Weight (lb.)” column shows that the weights range from 40.8 lbs. to 77.2 lbs.
- The lightest solar panel listed is the Seraphim N-TOPCon SRP-440-BTD-BG at 40.8 lbs.
- The heaviest solar panel listed is the Waaree WSMT-700 N-Type TOPCon at 77.2 lbs
Our data shows solar panels’ typical weight range is approximately 44 and 55 lbs.
Factors that could influence a solar panel’s weight include:
- Size: Larger panels with more surface area will generally be heavier.
- Materials: The type and thickness of materials used in the panel’s construction (such as the frame, glass, and back sheet) will affect its weight.
- Type of Cells: Different types of photovoltaic cells may vary in weight.
Analyzing the Relationship Between Panel Size and Power Output
Our analysis presents a wealth of data on various solar panel models, which helps us understand the connection between panel size and power output.
- General Trend: The data suggests a general trend of larger panels producing more power. This aligns with the understanding that a greater surface area can accommodate more photovoltaic cells (the components responsible for converting sunlight into electricity).
- Dimensions and Area: The dimensions of each solar panel model are listed in millimeters, along with the calculated area in square meters. Looking at the “Dimensions (mm),” “Area (m²),” and “Power Range (W)” columns makes it easy to compare the panels. For instance:
- The Aptos DNA-108-BF10 measures 1722 x 1134 x 35 mm, has an area of 1.95 m², and has a power range of 400-410 W.
- The Waaree WSMT-700 N-Type TOPCon features larger dimensions (2384 x 1303 x 35 mm), a greater area (3.11 m²), and a notably higher power range (680-715 W).
- Power Density: The “Power Density (W/m²)” gives us a more precise power output measure relative to the panel’s size. This metric helps account for variations in panel efficiency. Generally, larger panels have a similar or slightly lower power density than smaller panels, suggesting that while larger panels produce more total power, they aren’t necessarily more efficient at using their surface area.
- No Strict Proportionality: It’s important to recognize that the relationship between size and power output is not strictly proportional. Other factors—like the type and efficiency of the photovoltaic cells, manufacturing processes, and even the panel’s bifaciality—contribute to its power generation capabilities.
While our data analysis doesn’t explicitly state the relationship between panel size and power output, the data suggests a general positive correlation, with larger panels typically yielding higher power output.
The data suggests that various factors influence the relationship between panel size and power output, so this relationship shouldn’t be considered a rigid rule. Understanding how these factors work together is important for making informed decisions about solar panel choices.
Examining the Relationship Between Bifaciality and Solar Panel Weight
Non-bifacial solar panels are, on average, slightly lighter than bifacial panels, with non-bifacial panels weighing approximately 22 kg or 48.5 lbs. on average and bifacial solar panels weighing an average of about 24 kg, or about 53 lbs.
This weight difference is likely due to bifacial panels’ design and materials, since they need to allow light to pass through from both sides and the rear side needs protection.
Based on the available data, we can’t conclusively determine a correlation between solar panel bifaciality and weight. To better understand this potential relationship, we would need further information and analysis that focused on the design and material differences between bifacial and monofacial panels.
For example, it would be helpful to understand whether bifacial panels require additional materials or different construction techniques that could influence their weight
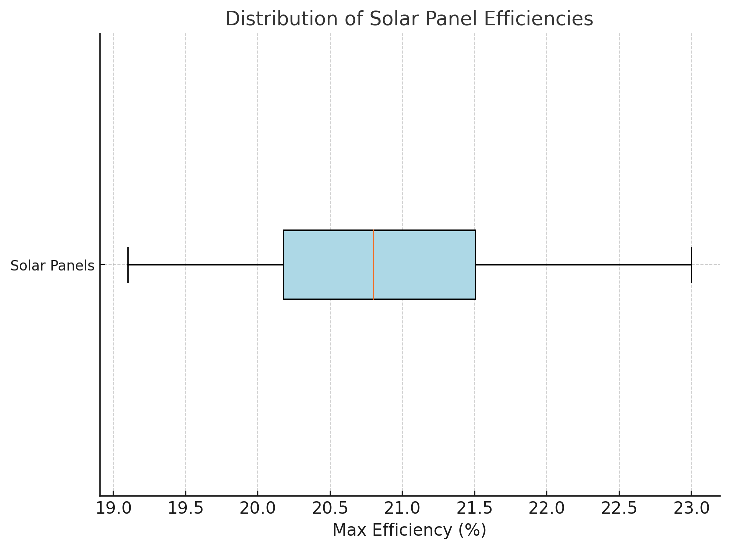
Identifying the Solar Panel Model with the Highest Maximum Efficiency
Our data comprises a comprehensive list of solar panel models and their corresponding maximum efficiency ratings.
The “Max Efficiency (%)” column identifies the solar panel models with the highest maximum efficiency: the Maxeon SPR-MAX6 and Canadian Solar CS6.1-54THM, at 23%. This means that these specific models can convert up to 23% of the sunlight they receive into usable electricity.
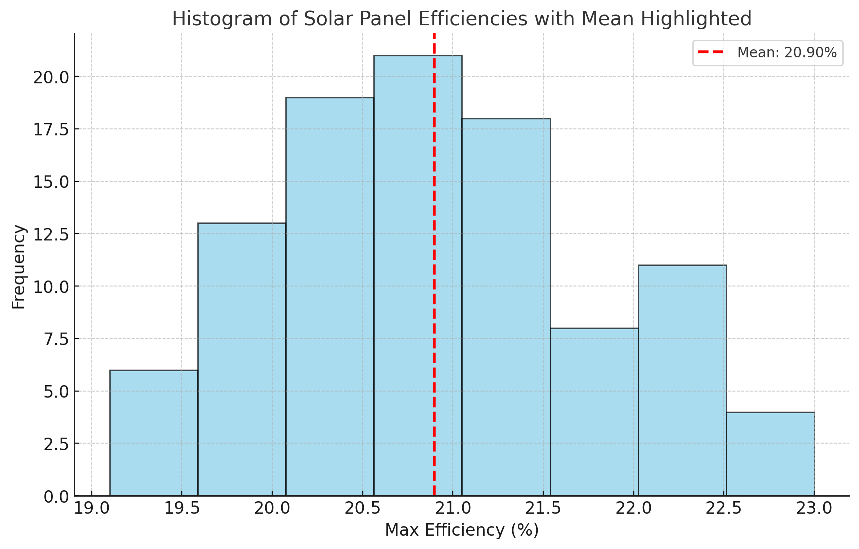
Other high-efficiency solar panels from our data include:
- REC Solar AA Pure-RX: This model has an impressive maximum efficiency of 22.6%.
- Seraphim N-TOPCon SRP-630-BTZ-BG and Seraphim N-TOPCon SRP-440-BTD-BG: Both models achieve a maximum efficiency of 22.5%.
- Waaree WSMT-700 N-Type TOPCon: This model features a maximum efficiency of 22.5%.
While efficiency is a critical factor in solar panel performance, you should also factor in other considerations, like power output, size, weight, and cost into your decision-making process.
Identifying the Solar Panel with the Highest Power Density
According to our analysis, the Jinko HL-4-B model has the highest power density at 222.5 W/m².
Power density represents the power output per unit area of the panel, and it’s an important metric for evaluating a solar panel’s efficiency at using its surface area to generate power. In this case, the Jinko HL-4-B panel can generate 222.5 watts of power for every square meter of its surface.
The Jinko HL-4-B achieves its high power density through advanced photovoltaic cell technology and a design that maximizes the panel’s surface area. The cells within the panel are highly efficient, allowing them to generate more electricity from the same amount of space. As a result, this panel can produce more power relative to its size compared to other panels.
Correlations between Solar Panel Attributes and Power Output
Analyzing this data reveals some correlations between these factors.
- Size and Power Output: Generally, larger solar panels have higher power output. This is because a larger surface area allows for more photovoltaic cells responsible for converting sunlight into electricity.
- Efficiency and Power Density: Solar panel efficiency, measured as a percentage, represents how effectively the panel converts sunlight into electricity. Panels with higher efficiency can generate more power from the same amount of sunlight. Power density, measured in watts per square meter (W/m²), indicates the power output relative to the panel’s surface area. Higher efficiency often translates to higher power density.
- Weight and Power Output: There is no direct correlation between the weight of a solar panel and its power output. While larger panels tend to be heavier due to more materials, weight alone doesn’t determine power generation capabilities.
- Bifaciality: Some solar panels are bifacial, meaning they can generate electricity from both sides. This can increase their power output compared to traditional, single-sided panels.
Manufacturers Offering Solar Panels Exceeding 500W
Based on our list, only two manufacturers offer panels that exceed 500W:
- Aptos: The Aptos DNA-144-BF10-550W-DG model boasts a power output of 550-550W.
- Waaree: Waaree offers two models surpassing the 500W threshold: the Waaree Bi-55-550 Dual Glass with a power output of 550-550W, and the Waaree WSMT-580 TOPCon N-Type with a power output of 580-580W.
Higher wattage panels generally indicate a larger surface area and potentially more advanced photovoltaic cell technology. This can translate to increased energy generation capacity for a given installation area. Factors such as efficiency, cost, and installation requirements should also be considered when selecting solar panels for a specific project.
Advantages and Considerations of High-Wattage, Bifacial, and Larger Panels for Commercial Solar
Higher wattage panels and bifacial panels can offer advantages in commercial applications.
Higher Wattage
- Cost Efficiency: Higher wattage panels can contribute to lower installation costs per watt, as fewer panels, racking components, and labor are required. This is a significant advantage in large-scale commercial projects where minimizing installation expenses is essential.
- Energy Production: Panels with higher wattage naturally produce more electricity from the same amount of sunlight. This helps maximize energy generation in commercial settings with limited roof space or ground area.
Examples from the Sources:
- The Waaree WSMT-700 N-Type TOPCon (680-715W) stands out as a high-wattage option that could significantly benefit commercial projects.
- Other high-wattage panels include the Seraphim N-TOPCon SRP-630-BTZ-BG (630W), the Waaree WSMT-580 TOPCon N-Type (580W), and the Aptos DNA-144-BF10-550W-DG (550W).
Bifacial Technology
- Increased Energy Yield: Bifacial panels capture sunlight from both sides, increasing energy production compared to monofacial panels. This is particularly beneficial in commercial settings where ground or roof surfaces can reflect sunlight onto the back side of the panels.
- Site Suitability: The effectiveness of bifacial technology depends on the reflectivity (albedo) of the surrounding surfaces. Like white roofs or gravel, lighter-colored surfaces reflect more sunlight, enhancing bifacial panel performance.
Examples from the Sources:
Several bifacial panels are included in the sources, including models from
- Longi (e.g., LR6-72HBD),
- REC Solar (e.g., AA Pure-RX)
- VSUN Solar (e.g., 108BMH).
Larger Panel Size
- Fewer Installations: Larger panels allow for achieving a higher power output with fewer installations. This simplifies installation logistics and potentially reduces labor costs, which is advantageous in commercial projects.
- Potential Trade-offs: It’s important to note that larger panels might have limitations regarding transportation, handling, and roof load capacity.
Examples from the Sources:
- The Longi LR4-72HBH and Canadian Solar CS3W, as you mentioned, are examples of larger panels suitable for commercial installations. Their dimensions fall within the ranges you provided, offering excellent power output.
Concluding Insights
Our study concludes that solar panel dimensions are not uniform and are subject to variations based on numerous factors. While the data presented offers a comprehensive look at the ranges for length, width, and depth across various manufacturers and models, understanding the reasons behind these variations is important.
- Wattage heavily influences panel dimensions. As the wattage of a solar panel increases, so too does its physical size. This is because higher-wattage panels contain more photovoltaic cells to generate more electricity. The data showcases this trend, with lengths exceeding 82.7 inches becoming more common for higher-wattage models.
- Panel technology plays a role in determining size. Different types of solar cells and panel construction techniques can lead to variations in dimensions. For instance, panels utilizing newer, more efficient cell technologies may achieve higher wattages within a smaller footprint compared to older technologies.
- The intended application of a solar panel can also impact its size. Specialized panels designed for unique applications, like off-grid systems or portable solar chargers, may deviate from typical dimensional ranges to suit specific requirements.
Recognizing that solar panel dimensions are not one-size-fits-all is paramount. The data highlights the importance of considering individual project needs and consulting manufacturer specifications to determine the most suitable panel dimensions for a particular application.